다익스트라
Updated:
-
다익스트라(dijkstra)
음의 가중치가 없는 그래프에서 시작점을 기준으로 다른 모든 노드까지의 최단거리를 구하는 알고리즘이다. 방향그래프, 무방향 그래프 모두 상관 없지만, 가중치가 음수인 edge가 단 하나라도 존재하면 다익스트라를 사용할 수 없다. 시간복잡도는 이다.
-
예시
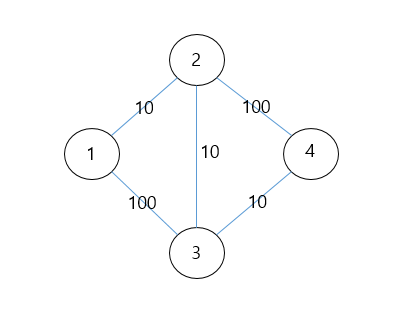
시작점은 1일때 기준
시작점 1에 연결된 노드 2, 3을 큐에 넣고 가장 cost가 작은 2(10)이 dist[2] = 10으로 갱신된다.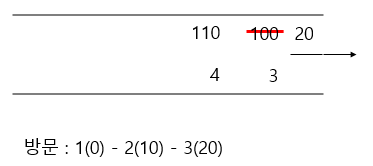
노드 2에 연결된 노드 4가 큐에 들어가며 3의 cost 100이 20으로 업데이트 되고 dist[3] = 20으로 갱신된다.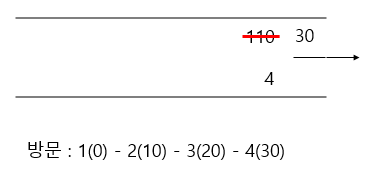
마지막으로 노드 3에 의해 노드 4의 cost가 110에서 30으로 업데이트 되며 최종 dist[4] = 30으로 갱신된다.
- 코드 구현(C++)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10
typedef pair<int, int> P;
int dist[MAX];
bool visited[MAX];
vector<P> v[MAX];
void dijkstra(int start) {
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P>> pq;
dist[start] = 0;
pq.push({ 0, start });
while (!pq.empty()) {
int now;
do {
now = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
} while (!pq.empty() && visited[now]);
if (visited[now]) break;
visited[now] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < v[now].size(); i++) {
int next = v[now][i].first;
int d = v[now][i].second;
if (dist[next] > dist[now] + d) {
dist[next] = dist[now] + d;
pq.push({ dist[next], next });
}
}
}
}
int main(void) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) dist[i] = INT_MAX;
v[1].push_back({ 2, 10 });
v[1].push_back({ 3, 100 });
v[2].push_back({ 1, 10 });
v[2].push_back({ 3, 10 });
v[2].push_back({ 4, 100 });
v[3].push_back({ 1, 100 });
v[3].push_back({ 2, 10 });
v[3].push_back({ 4, 10 });
v[4].push_back({ 2, 100 });
v[4].push_back({ 3, 10 });
dijkstra(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) cout << dist[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
-
결과
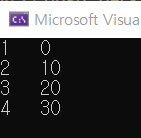
시작점 1일때
1 -> 1 : minimun cost(0)
1 -> 2 : minimun cost(10)
1 -> 3 : minimun cost(20)
1 -> 4 : minimun cost(30)
